Enterprises are turning to private networks to drive their digital transformation. By leveraging private network technologies, industry verticals can create intelligent, dynamic, and flexible systems that offer a range of benefits, including speed, reliability, low latency, security, mobility, and indoor and outdoor coverage. However, enterprises cannot always access licensed spectrum and public networks do not always meet the coverage and reliability requirements of complex enterprise environments.
Status of locally licensed, shared, and unlicensed spectrum
Spectrum is a necessary piece for deploying private networks. The management of spectrum is typically categorized into three types:
- Horizontal sharing, which can allow exclusivity for spectrum access. In this case, the use of spectrum is coordinated and locally licensed spectrum is an example.
- Vertical sharing, where spectrum usage occurs according to different priority levels. Higher priority must be protected from harmful interference from usage at lower priority. This approach is used in the US 3.5 GHz CBRS band, which has three priority layers.
- Unlicensed spectrum, where spectrum is shared dynamically with mitigation techniques for interference, such as Listen-Before-Talk and power restrictions.
Shared spectrum access is managed by the local government and other regulatory bodies. For example, the US has dedicated the CBRS band for private network deployments. Germany, Japan, the UK, Denmark, and others have also allocated specific spectrum bands for private networks.
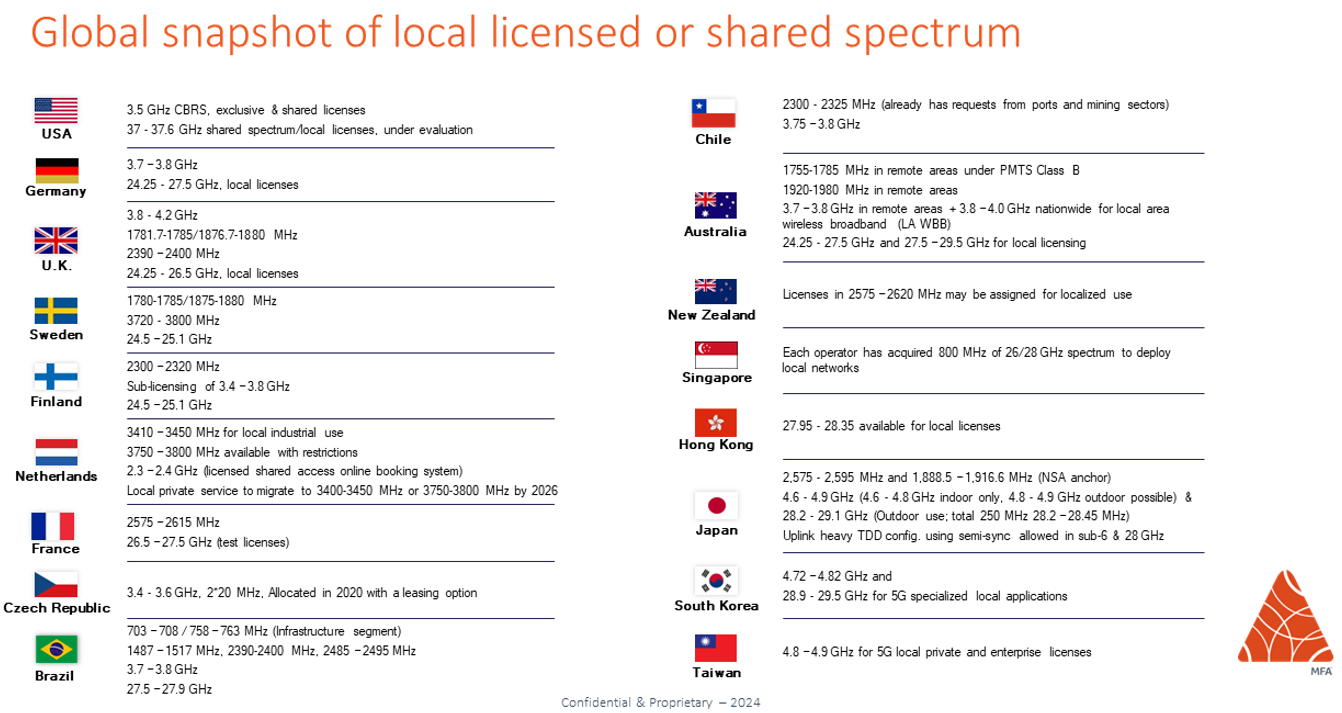
Figure 1: A Global Snapshot of local licensed or shared spectrum available for private network deployments
Leveraging licensed, shared, and unlicensed spectrum
Shared or licensed spectrum alone cannot serve all the use cases needed in industry verticals. Unlicensed spectrum combined with licensed spectrum can provide enterprises with increased efficiency, flexibility, and reduced cost.

Figure 2: Unlicensed spectrum availability worldwide.
Technical challenges of spectrum allocation
Unfortunately, many countries have not made licensed spectrum available for private networks, leading to a lack of coordination on spectrum availability and challenges for enterprises looking to deploy private networks across different countries.
As part of our goal to promote the global industry adoption of private networks, we encourage regulators and other governing bodies to make spectrum available to fit a wide range of use cases, performance, and deployment. By considering the following framework, regulators can stimulate access to and meet the growing need for private mobile networks across industry verticals:
- Lower the barrier to entry of spectrum access by facilitating timely access to affordable quality spectrum to meet the increasing needs and use cases.
- Promote the development and testing of innovative use cases and services by opening access to new spectrum bands by issuing test licenses.
- Advance regulatory actions that facilitate a level playing field to local network operators with different stakeholder saliences.
- Provide improved flexibility and scalability required by the novel use cases through varying service level parameters and customer value.
- Develop and utilize automated authorization and spectrum management processes to deliver timely and equal opportunity access and high efficiency for network deployments.
- Support the creation of automated marketplaces to stimulate the reuse of unused spectrum resources and reduce transaction costs associated with spectrum leasing.
- Encourage researchers to develop technical solutions that address real-life spectrum access challenges in specific bands with incumbent systems by promoting the sharing of knowledge.
Read the Characterization of regulatory frameworks for spectrum access in local mobile communication network deployments article via IEEE Xplore to learn more about this topic.
Alliance for private networks resources
The Alliance for private networks is championing the global industry adoption of private networks by educating the ecosystem and providing publicly available tools that ease deployment, such as:
- The Uni5G™ technology blueprints, which leverage 3GPP 5G standards to define profiling and classification requirements, enabling industry verticals to efficiently deploy their own optimized, reliable, and secure 5G private network.
- A unique global PLMN-ID, which simplifies the path to private network deployment in any available spectrum and accelerates the ecosystem.
- An interactive spectrum map that allows enterprises to identify the available spectrum for their individual country and/or region. Based on data gathered from Alliance member companies and their specialists, our interactive spectrum map provides global tracking of available locally licensed, shared, and unlicensed spectrum bands.
To learn more about the resources and tools we provide for private network deployments, visit www.mfa-tech.org.

